Linux - Disk Space Management with Quotas
Published on

Contents
Introduction
Any resource that is going to be shared has to be administrated, and it varies depending on how many users use it.
Establishing a Quote System allows restricting/limiting the abuse of the resources. For example, Google Drive free plan limits users to 15 Gb., while educational organizations doesn’t have this restriction.
This Quotas can be CPU or Storage measured.
Every OS needs at least between 10% and 15% of free disk space to work fine.
Checking storage
Commands
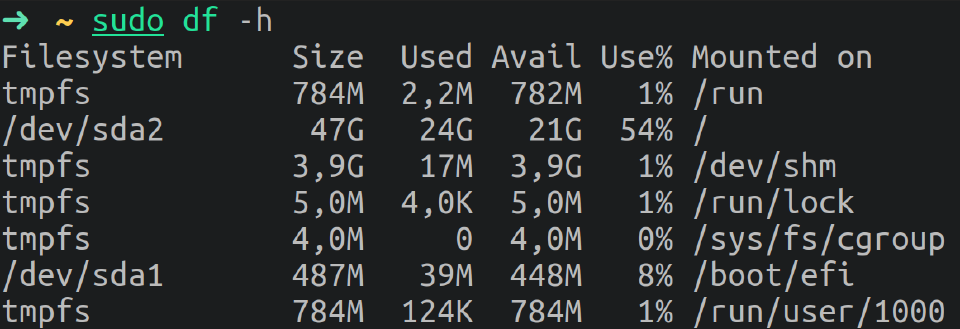
The following commands are used to check the used/free space of filesystems:
df: Shows a report of the disk space usage by each filesystem.fdisk -lallows the same.
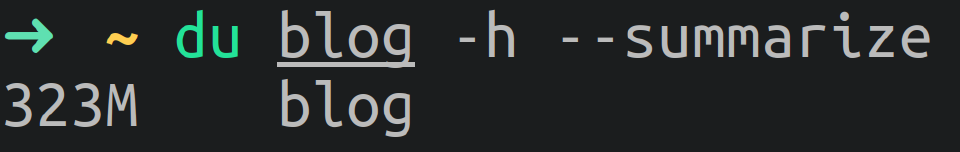
du: Estimates the Disk Usage of each file in the directory (recursively).
Exercises
To check the max free number of files (inodes) and the blocks that can still be written we can check the superblock with:
$ sudo tune2fs -l /dev/sda2 | grep "Free "
Free blocks: 6318621
Free inodes: 2852049
To check how much space is used by /home directory:
$ du -sh /home
8,4G /home
Quote System
Quotas are necessary as in a multi-user system limits allow to distribute space to each user. This way, everyone has the same conditions. As administrators, we don’t want a user to upload all his movies to the system and block system resources for other users.
Quote Systems are only for filesystems, not directories, and can be applied to users or groups.
They have two modes to limit the use of the disk:
- inodes: Max number of files.
- blocks: Max size.
There are two limits:
- Soft limit: Informative limit. Where the user is told to be careful of how much data they have. Less than Hard Limit.
- Hard limit: Real limit. At this point, the user is not allowed to write any data on the filesystem.
Grace period
A grace period allows blocking usage from a user after the Soft Limit. This block can occur when the period is over, or when the user reaches the Hard Limit. By default, the grace period for blocks and inodes is 7 days.
To set the maximum time after the user surpassed the soft limit:
edquota -t
If the grace period is set to 0, the user can pass the Soft limit all the way to the Hard limit. If the grace period is set to any value other than 0, the user that surpasses the Soft limit will have a limited time to keep those files until the system stops him.
Inconvenients
When a quota system is implemented, more or less a 30% of performance loss is expected due to constantly checking the space usage of a logged-in user.
To solve this is important to have a good division of the filesystem, limiting performance loss.
If a user doesn’t have a quota assigned, is assumed that it doesn’t have delimited storage.
Commands
quotaon: Sets on the quota.quotaoff: Sets off the quota.setquota: Sets a quota.setquota -u peter 100M 200M 0 0 /
edquota: Allows to edit “adquota” files (in/) to set quotas. It’s easier to use compared withsetquota.quotaandrepquota: They show info about quotas and a report of the space consumed by each user and group.quota -u usershows info about space used of a specific user.
quotacheck: Runs over the filesystem block by block checking free and occupied inodes. Usually runs at boot.
Installation
Install quota:
sudo apt install quota
Edit etc/fstab, adding usrquota,grpquota before the errors=.... Leave no blank spaces!!
# /etc/fstab: static file system information.
#
# Use 'blkid' to print the universally unique identifier for a
# device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices
# that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5).
#
# <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
# / was on /dev/sda2 during installation
UUID=d5a25364-33cf-4fc6-a71a-da6861bfdbfe / ext4 usrquota,grpquota,errors=remount-ro 0 1
Sets on the quota:
quotacheck -gum /
# -g : User quotas listed in the filesystems specified are to be checked.
# -u : Group quotas listed in the filesystems specified are to be checked.
# -m : Don't try to remount filesystem read-only
To set a quota to a user:
edquota -u user
Change here the soft and the hard limit of the blocks or the inodes. As blocksize is measured in Kb, so 50 Mb are 51200 blocks.
Use this formula:nº of blocks = nº of Mb · 1024
To copy a quota from a user to another user:
edquota -u -p firstUser endUser
- Reboot
- Check that user has the quota applied with:
sudo repquota -u user
To check the soft/hard limit is applied, we can generate a file with a similar space:
dd if=/dev/zero of=BIGFILE.iso bs=1M count=30000 # 30 Gb
Check again for surpassed quotas:
sudo repquota /